The Opportunity Economy is the next Industrial Revolution
Challange is designing social transformation in nation where the average literacy needs to be increased.
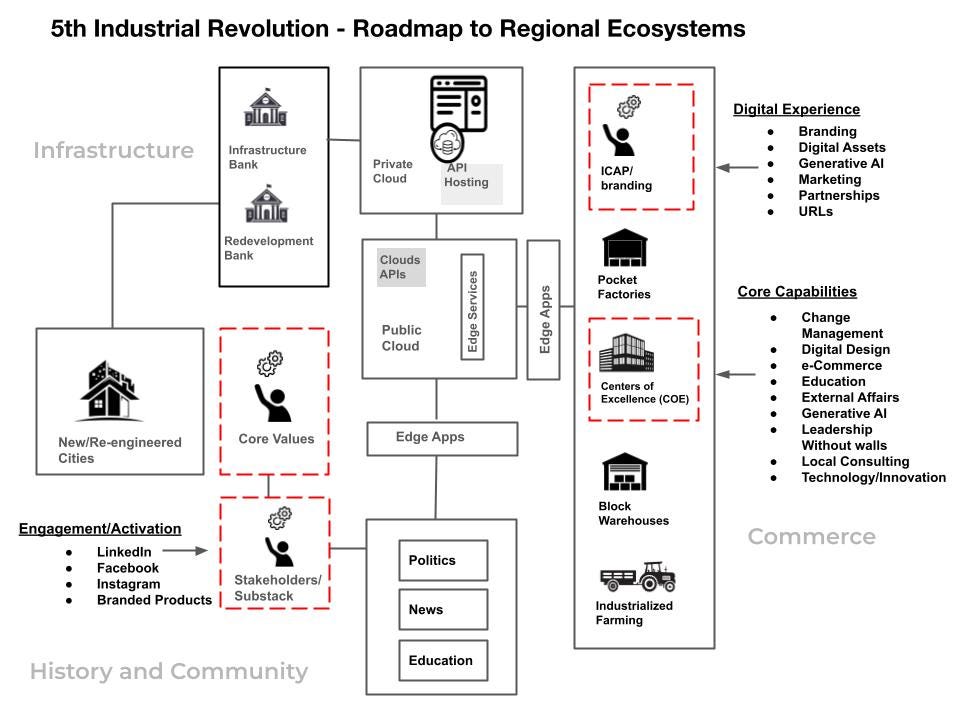
The Opportunity Economy is the 5th Industrial Revolution. (This short extract is created from a larger white paper.)
Opportunity Economy
1. Purpose and Context
The opportunity economy is designed to address the declining middle-class buying power, recognizing that traditional capitalism, as defined by Adam Smith in Wealth of Nations, cannot scale effectively for the middle class. This ecosystem creates a parallel structure to legacy capitalism with the specific aim of sustaining and growing the middle class by incorporating the efficiencies of AI to do more with less to create a sustainable form of capitalism.
1.1 Problem Statement:
An example of the shrinking middle class—imagine an economy with 10 people where the cost of a hamburger is $1. Wall Street continually demands higher earnings each year. Now, assume 4 people fall out of the middle class due to retirement, layoffs, or illness. The remaining 6 must pay more for the same hamburger to meet Wall Street's profit expectations. This highlights the pressure on the shrinking middle class and the resulting pressure on prices across the economy.
2. Goals of the Opportunity Economy Model
2.1 AI for Efficiency and Scaling:
Goals: Leverage AI to increase productivity, reduce costs, and enable the opportunity economy to scale by doing more with less.
Value: AI integration ensures economic scaling with reduced operational burden, allowing businesses and communities to produce more efficiently.
2.2 Sustain Middle-Class Buying Power:
Goals: Prioritize sustaining and growing middle-class buying power.
Value: Protecting middle-class purchasing power stabilizes consumer demand, ensuring long-term economic growth and prosperity for the majority of the population.
2.3 Operate Alongside Legacy Capitalism:
Goals: Create a parallel model to legacy capitalism that supports middle-class growth and contributes to overall GNP without dependence on Wall Street.
Value: Building an economic system that complements traditional capitalism provides resilience, reducing reliance on stock market volatility.
2.4 Community-Driven Capitalism:
Goals: Focus on community ownership and localized economic growth as a more sustainable and equitable model.
Value: Encourages equitable distribution of wealth by promoting local investment and empowerment, leading to stronger, self-sufficient communities.
2.5 Alternative Capital Formation:
Goals: Develop community-driven financial systems that emphasize long-term growth over short-term stock market returns.
Value: Reduces economic dependency on Wall Street by fostering sustainable, long-term investments that benefit local economies.
3. Issues and Solutions
3.1 Average Literacy Level:
Many individuals may lack the advanced literacy or technical skills for engaging with AI-driven tools or navigating complex financial models.
Solution: Implement educational programs and upskilling initiatives within community tech hubs.
Value: Boosts community participation in the economy by ensuring equitable access to new technologies and financial tools.
3.2 Access to Technology:
Inequities in access to technology and high-speed internet may prevent some communities from benefiting equally from AI-driven platforms and tech hubs.
Solution: Invest in digital infrastructure to ensure equitable access across urban and rural areas.
Value: Levels the playing field, ensuring all communities can fully participate in and benefit from technological advancements.
3.3 Cultural Resistance:
Resistance to shifting from traditional capitalist models to community-driven models may arise, especially in areas where Wall Street's influence is strong.
Solution: Community engagement campaigns to raise awareness and demonstrate the benefits of this new economic structure.
Value: Fosters a smoother transition by educating communities on the long-term advantages of a community-driven economic approach.
3.4 AI Trust and Adoption:
Some communities may be skeptical of AI due to fears of job loss or mistrust in the technology.
Solution: Develop transparency and trust-building programs to show AI’s role in enhancing middle-class jobs.
Value: Builds trust in AI as a tool for growth and opportunity rather than displacement, increasing adoption and innovation.